E-invoicing
Introduction
The GST Council has approved the implementation of e-Invoicing or electronic invoicing in a phased manner for reporting of Business to Business (B2B) invoices to GST System, starting from 1st Jan, 2020 on voluntary basis. Being the 1st Invoice Registration Portal (IRP), National Informatics Centre (NIC), has made the e-Invoice registration services available through API mode, in addition to other modes. The tax payers and GST Suvidha Providers can integrate their business systems and processes with the e-Invoice system through these APIs for seamless registration of the invoices, generated/prepared on their systems. To know more about the e-invoicing system click here.
Workflow of e-Invoice System
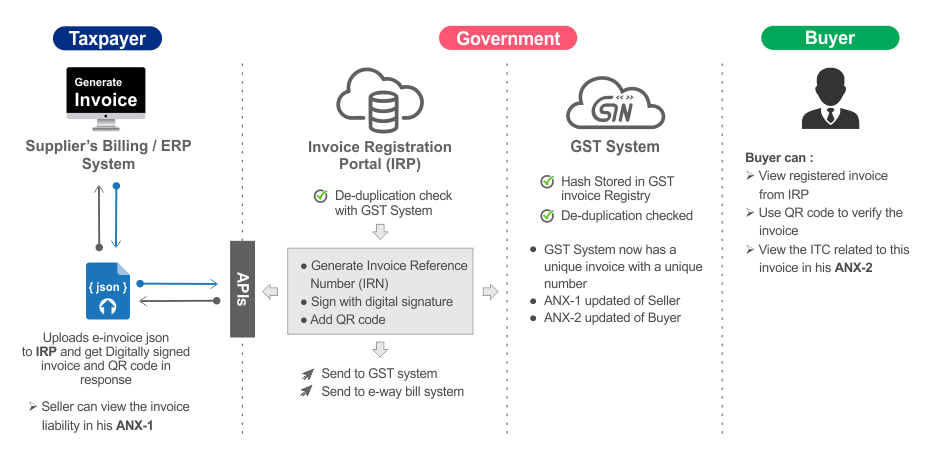
Need of e-Invoicing System
If an invoice is generated by software on the computer or a machine then does it become an e-invoice? Is e-invoice as a system where taxpayers can generate the invoices centrally? Many such questions are raised when e-invoice gets discussed.
E-invoice does not mean generation of invoices from a central portal of tax department, as any such centralization will bring unnecessary restriction on the way trade is conducted. In fact, taxpayers have different requirements and expectation, which can’t be met from one software generating e-invoices from a portal for the whole country. Invoice generated by every software may look more or less same; however, they can’t be understood by another computer system even though business users understand them fully. There are hundreds of accounting/billing software which generate invoices but they all use their own formats to store information electronically and data on such invoices can’t be understood by the GST System if reported in their respective formats.
Hence a need was felt to standardize the format in which electronic data of an Invoice will be shared with others to ensure there is interoperability of the data. The adoption of standards will in no way impact the way user would see the physical (printed) invoice or electronic (ex pdf version) invoice. All these software would adopt the new e-Invoice standard wherein they would re-align their data access and retrieval in the standard format. However, users of the software would not find any change since they would continue to see the physical or electronic (PDF/Excel) output of the invoices in the same manner as it existed before incorporation of e-Invoice standard in the software. Thus the taxpayer would continue to use his accounting system/ERP or excel based tools or any such tool for creating the electronic invoice as she is using today.
Taxpayer can enter the invoice details in bulk generation tool available on e-invoice portal which in turn will create JSON file for uploading on the e-invoice system.
E-Invoice and Tax Department
The e-invoice system being implemented by tax departments across the globe consists of two important parts namely,1) Generation of invoice in a standard format so that invoice generated on one system can be read by another system.
2) Reporting of e-invoice to a central system.
The basic aim behind adoption of e-invoice system by tax departments is ability to pre-populate the return and to reduce the reconciliation problems. Huge increase in technology sophistication, increased penetration of Internet along with availability of computer systems at reasonable cost has made this journey possible and hence more than 60 countries are in the process of adopting the e-invoice. GST Council has given the responsibility to design the standard of e-invoice and update the same from time to time to GSTN which is the custodian of Returns and invoices contained in the same. Adoption of e-invoice by GST System is not only part of Tax reform but also a Business reform as it makes the e-invoices completely inter-operable eliminating transcription and other errors.
Invoice Reference Number (IRN)
The Invoice Reference Number (IRN) is a unique number (also known as hash) generated by the e-invoice system using a hash generation algorithm. For every document such as an invoice or debit or credit note to be submitted on the e-invoice system, a unique 64 character invoice reference number shall be generated.
The unique IRN will be based on the computation of hash of GSTIN of generator of document (invoice or credit note etc.), Year and Document number like invoice number. The hash could also be generated by the taxpayers based on above algorithm. This shall be unique to each invoice and hence be the unique identity for each invoice for the entire financial year in the entire GST System for a taxpayer.
QR Code
E-invoice system will generate a unique 64 character length Invoice Reference Number (IRN) and digitally sign the e-invoice and the QR code (Quick response Code). The QR code will enable quick view, validation and access of the invoices from the GST system from hand held devices.
The QR code will consist of the following e-invoice parameters:
- GSTIN of supplier
- GSTIN of Recipient
- Invoice number as given by Supplier
- Date of generation of invoice
- Invoice value (taxable value and gross tax)
- Number of line items.
- HSN Code of main item (the line item having highest taxable value)
- Unique Invoice Reference Number (hash)
The digitally sign QR code will have a unique IRN (hash) which can be verified on the central portal as well as by an Offline App by officer. This will be helpful for tax officers checking the invoice on the roadside where Internet may not be available all the time.
E-invoicing System under GST
The move will help in curbing Goods and Services Tax (GST) evasion through issue of fake invoices. Besides, it would make the returns filing process simpler for businesses as invoice data would already be captured by a centralised portal. The proposed 'e-invoice' is part of the exercise to check GST evasion. With almost two years into GST implementation, the government is now focussing on anti-evasion measures to shore up revenue and increase compliance.
There are over 1.21 crore registered businesses under the GST, of which 20 lakh are under the composition scheme. In order to ensure no duplication, e-invoice system will be closely connected to the GST system, which will be the central repository for all IRN generated. Given that GST system already has IRN data, populating of ANX 1 for the supplier will be possible.
Objective
E-invoicing in India will be a big move, due to the volume of business transactions undertaken every day, as well as the plethora of different, non-standardised formats used in invoice generation. The new e-invoicing system aims to make invoice reporting an integral part of a business process and to remove the tedious task of invoice-compilation at the end of a return period. Claiming fictitious Input Tax Credit (ITC) by raising fake invoices is also one of the biggest challenges currently faced by tax-authorities. The e-invoice system will help to curb the actions of unscrupulous taxpayers and reduce the number of fraud cases as the tax authorities will have access to data in real-time.
Stakeholders
The objective behind introducing e-invoice is to effectively address the expectations and concerns of the stakeholders by leveraging the use of ITC (Input Tax Credit).
Benefits of E-invoice System
The major benefits of e-invoice system are as follows:
- Standardization: One time reporting on B2B, B2G and export invoice data in the form it is generated to reduce reporting in multiple formats.
- Seamless Reconciliation: Reconciliation and data verification between suppliers and recipient will be seamless and thus provide better control over input tax credit computation and claim.
- Lesser Compliance: Reduction in overall compliance burden. Substantial reduction in input credit verification issues as same data will get reported to tax department as well to buyer in his inward supply (purchase) register. • Automation: Auto-generation of Sales and Purchase Registers (ANX-1 and ANX-2). To generate Sales and purchase register (ANX-1 and ANX-2) from this data to keep the Return (RET-1 etc.) ready for filing under New Return.
- Elimination of fake invoices: Reduction of tax evasion, System level matching of input credit and output tax.
- Information Availability: Near real-time availability of information to all the relevant participants in the supply chain.
- On receipt of info thru GST System as buyer can do reconciliation with his Purchase Order and accept/reject in time under New Return.
- Environment friendly – The need of the paper form of the multiple copies of way bill is eliminated. Hence, the tons of paper are saved per day.
- Officials saved of monotonous work collecting and matching the manual work with the returns of the taxpayers.
Benefits of E-invoice System
- Save time: With e-invoicing, many unnecessary steps are cut out of the invoicing process. Both you and your customer will be saving time using e-invoicing system.
- Reduce costs: With paperless invoicing, you do not have to pay for paper or for postal fees. Further, by saving time with e-invoicing instead of using templates and emailing PDFs, you save working time. Concentrate on other value-adding tasks instead. We all know time is money!
- Reduce mistakes: By minimizing manual input and increasing automation, mistakes and typos are reduced.
- Offer better customer service: It is more convenient for customer to get an e-invoice to their desired platform receiving an e-invoice instead of a paper invoice saves up to 90% on processing costs.
- Easier to keep track of invoices: Know when an invoice has been sent, viewed, and paid when using e-invoicing system. You will know for sure that the invoice is sent and received.
- A higher degree of control and insight into the invoicing process: If you use online invoicing software, everything is saved on one platform which is accessible from anywhere on any device.
Features
- User friendly System – The system is user friendly with lots of easy to use operations by the users.
- Easy and quick generation of methods – There are a number of methods are provided using which the users can easily and quickly generate the e-invoices.
- Multiple modes for e-invoice generation – This system support different modes of e-invoice generation. The user can register the mode of e-invoice generation and use them for invoice generation.
- Creating own masters – The user has a provision to create his own masters like customers, suppliers, products and transporters. The system facilitates to use them while generating the e-invoice.
- Managing sub-users – The taxpayer or registered person can create, modify and freeze the sub-users for generation of the e-invoice and assign them to his employees or branches as per need. This system also facilitates him to assign the roles/activities to be played by the sub-user on the system.
- Monitoring the IRN generated– The system facilitates the registered person to know the number of INR, generated by them on a specific date
- Generating the GSTR-1 from the e-invoices – Based on the e-invoice generated, the system pulls the GSTR-1 related information and pushes it to the taxpayers GSTR-1 returns. This avoids the taxpayers in uploading these transaction details.
- QR bar code on the e-invoice – The QR code on the e-invoice helps for easier and faster verification of the e-invoices.
FAQs
E-Invoicing System
- Business to Business Invoice
- Business to Government Invoices
- Export Invoices
- Reverse Charged Invoices
- Credit Notes
- Debit Notes
- The supplier has erroneously declared a value which is less than the actual value of the goods or services or both provided.
- The supplier has erroneously declared a lower tax rate than what is applicable for the kind of the goods or services or both supplied.
- The quantity received by the recipient is more than what has been declared in the tax invoice.
- Any other similar reasons.
- The supplier has erroneously declared a higher tax rate than what is applicable for the kind of the goods or services or both supplied.
- The quantity received by the recipient is less than what has been declared in the tax invoice.
- The quality of the goods or services or both supplied is not to the satisfaction of the recipient thereby necessitating a partial or total reimbursement on the invoice value.
Registration
Generation of IRN
Signed QR
- GSTIN of Supplier
- GSTIN of Recipient
- Invoice number as given by Supplier
- Date of generation of invoice
- Invoice value (taxable value and gross tax)
- Number of line items.
- HSN Code of main item (the line item having highest taxable value)
- Unique Invoice Reference Number (hash)
Cancellation of IRN
E-Invoice can’t be partially cancelled. It has to be fully cancelled. Cancellation has to be done as per process defined under Accounting Standards.
The e-invoice mechanism enables invoices to be cancelled. This will have to be triggered through the IRP, if done within 24 hours. After 24hours, the same will need to be done on the GST System.
User Management
Step 1: Click ‘Freeze Sub-user’ under the option ‘User Management’ on the left-hand side of the dashboard
Step 2: Select the sub-user you want to Freeze, the below screen opens up. Now click on ‘Freeze’ button appearing at the bottom of the screen. On clicking the ‘Freeze’ button, The sub-user will no longer be able to access any facilities on the e-invoice system.
Other modes of generation of IRN
- Web based
- API based
- Mobile app based
- Offline tool based and
- GSP based
- Login on the e-invoice portal using the username password and entering the captcha code.
- Select ‘Bulk Upload’ under 'E-Invoice' appearing on the left-hand side of the dashboard.
- Choose the saved JSON file from your system and click 'Upload’. After processing the JSON file the system generates list of e-invoice or error message.
- Generation of multiple IRN in one go
- It avoids duplicate keying in of the invoices to generate IRN
- It avoids the data entry mistakes while keying in for generation of IRN
- His invoicing system should be automated with IT solutions.
- He should be ready to change his IT system to integrate with E-invoice system as per API guidelines.
- His system should have SSL based domain name.
- His system should have Static IP Address.
- He should have pre-production system to test the API interface.
Miscellaneous
The e-invoice format primarily contains three parts:
- The e-invoice schema contains a list of technical field names, their descriptions, and a few other values with notes. It also specifies whether a field is mandatory or not.
- Masters will inform you about the inputs for specific fields as defined by the GSTN, like state code, invoice type, supply type, etc.
- The e-invoice template has been designed in compliance with GST rules. The mandatory fields are highlighted in green while optional ones are in yellow.
Here are some benefits for businesses if e-invoicing comes into play:
- E-invoicing solves the issue of data reconciliation, allows interoperability, and helps to eliminate errors during manual data entry.
- You can track the e-invoices, prepared by the suppliers, in real-time. This is possible only when the supplier has enabled the specific permission.
- An e-invoice system will make the process of filing tax returns easier. The details from the e-invoice will be auto-populated on tax return forms and while generating e-way bills.
- Frequent audits or surveys are unnecessary because all transaction details will be made available. The value of input credit and output tax can be matched by the system.
- Upon receiving a receipt of purchase via the GST system, the buyer can compare it with their purchase order and accept/reject the information under new returns.
- This initiative will also build efficiency within the tax administration by helping to identify fake invoices.
- Login on the e-invoice portal using the username password and entering the captcha code.
- Select ‘Print’ under 'E-Invoice' appearing on the left-hand side of the dashboard.
- Enter the 64 character length invoice reference number and click ‘Go’
- With the implementation of e-invoicing, tax authorities will have access to all their transactions as they have to be uploaded on the GST portal.
- Manipulating invoices will not be easy as they will have to be generated before the transaction takes place.
- The system will allow you to spot fake invoices easily by matching the input tax credit with the output tax details on the GSTN portal.
- e-Invoice Portal
- Zoho books
e-Way Bill
Introduction
Introduction of GST across India with effect from 1st of July 2017 is a very significant step in the field of indirect tax reforms in India.
For quick and easy movement of goods across India without any hindrance, all the check posts across the country are abolished.
The GST system provides a provision of e-Way Bill, a document to be carried by the person in charge of conveyance, generated electronically from the common portal.
To implement the e-Way Bill system, ICT based solution is required.
Hence, as approved by the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council, a web based has been designed and developed by National Informatics Centre (NIC) and it is being rolled out for the use of taxpayers and transporters.
The API interface based mechanism is also enabled for the tax payers to generate the e-way bills directly linking their system with e-Way Bill system.
To know more about API based interface mechanism of e-way bill system follow the link .
The intention of the implementation of E-Way Bill in place of road permit is
- Remove Physical Barriers at State Border.
- Reduce waiting time of vehicle at state border for checking.
- Track revenue leakage if any.
- No misuse of input tax credit (ITC)
- Reduction in Paper Work
- Uniformity Across Country
Waybill under Earlier VAT system
In order to monitor the bulk trade which necessarily takes place through trucks, it was mandatedunder VAT that each such consignment shall be accompanied by a ‘Delivery Note’ which were issued from the VAT offices to the taxpayers. At the end of every month the taxpayer had to submit an utilisation statement of the forms issued. The intention of the tax office was that to control the tax evasion being done by few of the tax payers. The taxpayer also used to facea great deal of hardship while seeking the blank Delivery Notesashe/she would have to make several visits to the tax office. At check-posts the trucks, would getdetained for a long time on frivolous grounds.Thus, it was a lose-lose situation for the trade as well as the government. In order to overcome these challenges, anew idea/system was introduced. In the new system, the taxpayer could upload the details of each transaction to the departmental ‘Server’ through the internet, and once uploaded the ‘Server’ would automatically generate a Delivery Note witha unique number, then this unique number could accompany the goods vehicle as a proof of having uploaded the transaction. Such a system would by itself ensurethat oncethe Delivery Note is issued there could be no possibility of tax evasion. It was one of the most successful and efficient system of prevention of tax evasion on one hand and an e-Governance initiative that provided the speedy and efficient services to the taxpayers on the other hand. This system was introduced and used by number of states.
E-Way Bill System under GST
Unique Selling Proposition (USP) of Goods and Services Tax is One Nation - One Tax – One Market. Introducing a separate way bill for each State under the GST system would definitely complicate the compliance and in turn affect the business of the taxpayers and transporters. Such a system of separate e-WayBill for each State would result in hindrance of movement of goods and free trade from one state to another. The State and Central Government officers will also find it difficult to cross-verify such e-WayBills if generated independently by each State. A new process is thus required which would ensure that a taxpayer, prior to movement of goods via a conveyance, would inform each transaction’s details to the tax department, obtain an acknowledgement number for having thus informed, and then use this acknowledgement number asa valid document accompanying the truck. The idea is that the taxpayer be made to upload the details of each transaction to a common portal through the Internet, and once uploaded, the common portal would automatically generate a document which can be tracked and verifiedeasily by any stakeholder.
E-Way Bill in GST Rule
- Information to be furnished by every registered person prior to commencement of the movement of goods and generation of e-WayBill.
- Upon generation of the e-Way Bill on the common portal, a unique e-Way Bill number (EBN) shall be made available to the supplier, the recipient and the transporter on the common portal.
- The person in charge of a conveyance shall carry — (a) the invoice or bill of supply or delivery challan, as the case may be; and (b) a copy of the e-Way Bill or the e-Way Bill number.
- The details of e-Way Bill generated shall be made available to the recipient, if registered, on the common portal, who shall communicate his acceptance or rejection of the consignment covered by the e-Way Bill.
- The information furnished while generating e-Way Bill such as 1) GSTIN of recipient 2) Place of delivery 3) Invoice Number 4) Invoice Date 5) Value of goods 6) HSN code etc. shall be made available to the registered supplier on common portal who may utilize the same for furnishing details in FORM GSTR-1.
- An officer authorised by the State can intercept any conveyance to verify the e-Way Billor the e-Way Bill number in physical form for all inter-State and intra-State movement of goods.
- A summary report of every inspection of goods in transit shall be recorded online by the proper officer in specified format within 24 hours of inspection and the final report in specified format shall be recorded within 3 days of the inspection.
- Where a vehicle has been intercepted and detained for a period exceeding thirty minutes, the transporter may upload the said information inaspecified format onthe common portal.
Objectives
- Single e-Way Bill for movement of the goods throughout the country.
- To prevent the evasion of tax.
- Hassle free movement of goods across India.
- Tracking the movement of goods with e-Way Bill number.
- Easier verification of the e-Way Bill by the officers.
Stakeholders
The objective behind introducing e-Way Bill is to effectively address the expectations and concerns of the stakeholders by leveraging the use of ICT.
The following are four key stakeholders of the e-Way Bill:- Suppliers – Generate the e-Way Bills and reject the e-Way Bills generated by other party against his/her name, if it does not belong to him/her.
- Recipients – Generate the e-Way Bills and reject the e-Way Bills generated by other party against his/her name, if it does not belong to him/her.
- Transporters – Generate the e-Way Bills, consolidated e-Way Bills and update the vehicle numbers for the e-Way Bills assigned to him for transportation by the taxpayers.
- Department Officers – Verify the e-Way Bills and consignments carried with the e-Way Bills.
Benefits of e-Way Bill system
The major benefits of e-Way Bill system are as follows:- The traders need not visit tax offices to collect and submit the Way Bill forms as used to be done in VAT regimes in some states.
- Average waiting time at mobile squad reduces drastically – As the verification of the e-Way Bill is done with the common portal, it will speed up the process of verification and allowing the vehicle to pass faster.
- Self-policing by traders- A trader while uploading gives the identification of the buying trader who will also account the transaction automatically.
- Environment friendly – The need of the paper form of the multiple copies of way bill is eliminated. Hence, the tons of paper are saved per day.
- Generation of GSTR-1 returns – GSTR-1 return of the supplier is auto prepared, hence he need not have to upload the same.
- Officials saved of monotonous work collecting and matching the manual way bill with the returns of the taxpayers.
Enhancements in e-Way Bill System
- Auto calculation of distance based on PIN Codes for generation of e-Way Bill.
- Knowing the distance between two PIN codes
- Blocking the generation of multiple e-Way Bills on one Invoice/Document.
- Extension of e-Way Bill in case the consignment is in Transit/Movement.
- Report on list of e-Way Bills about to expire.
- Registration of Transporters in Common Enrolment: Registered Transporters, which are having GSTIN in multiple states with same PAN, can use the common enrolment process.
Features of the e-Way Bill system
- User friendly System – The system is user friendly with lots of easy to use operations by the users.
- Easy and quick generation of methods – There are a number of methods are provided using which the users can easily and quickly generate the e-Way Bills.
- Checks and balances – The number of checks and balances have been introduced as per the requirements so that errors/mistakes of the users are eliminated.
- Multiple modes for e-Way Bill generation – This system support different modes of e-Way Bill generation. The user can register the mode of e-Way Bill generation and use them for e-Way Bill generation.
- Creating own masters – The user has a provision to create his own masters like customers, suppliers, products and transporters. The system facilitates to use them while generating the e-Way Bill.
- Managing sub-users – The taxpayer or registered person can create, modify and freeze the sub-users for generation of the e-Way Bill and assign them to his employees or branches as per need. This system also facilitates him to assign the roles/activities to be played by the sub-user on the system.
- Monitoring the e-Way Bills generated against me – The system facilitates the registered person to know the number of e-Way Bills, generated by other registered persons, against him/her. There is an option to user to reject these e-Way Bills, if they do not belong to him.
- Generating the GSTR-1 from the e-Way Bills – Based on the e-Way Bills generated, the system pulls the GSTR-1 related information and pushes it to the taxpayers GSTR-1 returns. This avoids the taxpayers in uploading these transaction details.
- Consolidated e-Way Bill – The system supports the transporters to prepare the consolidated e-Way Bill and hand over to the person in charge of the conveyance instead of giving the multiple e-Way Bills for movement of multiple consignments like parcel in one vehicle.
- Enabling the unregistered transporters to use e-Way Bill – There is a provision for unregistered transporters to enrol and create a user for him to generate the e-Way Bills and update the vehicle numbers.
- Common Enrolment – The system allow transporters who are GST registered to generate a Common Enrolment number which will allow them to generate one registration number for generating the e-way bills and updating Part-B throughout the country.
- Alerting the taxpayers – The system alerts and notifies the users through the web and SMS about the various activities like new notifications, rejected EWB, verified EWB, etc.
- QR bar code on the e-Way Bill – The QR code on the e-way bill helps for easier and faster verification of the e-Way Bill by the tax officers.
- Integrating with RFID for tracking the movement of the e-Way Bill – The provision has been made to integrate with the RFID for tracking the movement of e-Way Bill by the tax officers, without stopping the vehicle on the road.
Exemptions
An e-way bill is not required in the following cases:- If the value of the consignment is less than Rs. 50,000.
- When the goods being shipped are exempt from GST.
- If goods are transported by non-motorized conveyances (example: railways). Though an e-way bill is not required, an invoice or a challan should be carried during the transportation of goods.
- If goods are transported from a port, airport, air cargo complex or land customs station to an inland container depot or a container freight station for clearance by the Customs Department.
- Transport of goods as specified in Annexure to Rule 138(14) of the CGST Rules, 2017.
Blocking/Unblocking of E-Way Bill Generation
If the GST registered taxpayer has not filed Return 3B for the last two successive months in GST Common portal, then that GSTIN will be blocked for further generation of e-way bill either as Consignor, Consignee or Transporter. Once the Return-3B is filed in the GST Common Portal, the blocked GSTIN will get automatically updated as ‘Unblocked’ within a day in the e-Way bill system and the tax payer can continue with e-way bill generation. To know more about this click here.FAQs
General
E-way bill is a document required by a person in charge of the conveyance carrying any consignment of goods of value exceeding ₹ 50,000 as mandated by the Government. It is generated from the GST Common Portal for E-Way bill system by the registered persons or transporters who cause movement of goods before commencement of such movement.
The consignor or consignee, as a registered person or a transporter of the goods can generate the e-way bill. The unregistered transporter can enroll on the common portal and generate the e-way bill for movement of goods for his/her clients. Any citizen, other than the above, can also generate the e-way bill for movement of goods for his/her own use.
Note: The consignor can authorize the transporter/courier agency/e-commerce operator to fill PART-A of the e-way bill on their behalf.An e-way bill should be generated irrespective of the value of the consignment (even if the value is lesser than Rs.50,000) in two cases:
- When the goods are supplied by a principal to a job worker in an inter-state transaction.
- During an inter-state transfer of handicraft goods by a supplier who has been exempted from GST registration.
- Web-based system
- SMS-based facility
- Android app for generating and sharing e-Way bills (available only for taxpayers and enrolled transporters)
- Bulk generation
- Site-to-site integration
- GSP (Goods and Services Tax Suvidha Provider)
- If non-motorised conveyances such as railways are being used to transport goods. Although an e-Way bill is not required here, an invoice or a challan must be carried during transportation.
- If goods are shifted from a port, airport, air cargo complex or land customs station to an inland container depot or station for clearance by the Customs Department.
- If goods specified in Annexure to Rule 138(14) of the CGST Rules, 2017 are being moved.
The pre-requisite for generation of eway bill is that the person who generates eway bill should be a registered person on GST portal and he should also register in the eway bill portal. If the transporter is not a registered person under GST it is mandatory for him/her to get enrolled on e-waybill portal before generation of the e-way bill.
The transporter must carry an invoice, bill of supply, or delivery challan and a transporter’s ID along with the goods they are moving and he must be available with the person who is generating the e-way bill.
(1) Part A contains GSTIN of the recipient, Place of delivery (PIN Code), Invoice/Challan number and the date of issue, Value of goods, HSN code, Transport document number (Goods Receipt Number /Railway Receipt Number/Airway Bill Number/Bill of Lading Number), Reasons for transportation.
(2) Part B contains the details of the transporter (example: their Vehicle Number, LR Number etc.)
An e-way bill is generated for:
- Supply of goods
- Non-supply transactions like export/import, return of goods, job work, line sales, sale on approval basis, semi or completely knocked down supply, supply of goods for exhibition or fair, and goods used for personal consumption.
- An authorized officer may halt the vehicle to check the e-way bill or see the e-way bill number on paper.
- Verification of the e-way bill may be done through a Radio Frequency Identification Device (RFID), if the e-way bill has been mapped with RFID.
Note: If goods are transported for a distance less than 10 km within the State or Union territory from the business place of the transporter finally to the business place of the consignee, then it is not mandatory to update the details of the vehicle in the e-Way Bill.
Also, the supplier must take care to issue:
- A complete invoice before dispatching the first consignment.
- A delivery challan for each consignment along with a certified copy of the invoice.
- The original copy of the invoice, to be sent along with the last consignment.
Registration And Enrolment
All registered taxpayers under GST must register on the e-Way bill portal using their GSTIN.
Once the GSTIN is entered, the system sends an OTP to the registered mobile number for authentication and asks to create an account and start generating an e-Way bill.
A TRANSIN or Transporter ID is a unique 15-digit number which is generated by the e-Way bill system for an unregistered transporter. It is based on the state code, PAN, and Check code and can be shared among other individuals who are part of the transaction. The Transporter ID can be used to identify an unregistered transporter and assign an e-Way bill to them, instead of the GSTIN which is used by registered transporters.
Transporters can enrol themselves here.
Contents
- Part A contains the GSTIN of the recipient, place of delivery, invoice/challan number, value of the goods, HSN code, transport document number and the reason for transportation.
- Part B contains details about the transporter, such as their vehicle number.
- The first two letters of the vehicle number, from the left, indicate the state to which it is registered.
- The next two numbers are the sequential numbers of the district.
- The final four-digit number is unique to each vehicle.
- These three parts are put together to make the vehicle number.
Updating And Editing
Validity of an e-way bill
Validity is calculated based on the distance travelled.
Other than Over Dimensional Cargo vehicles| Distance | Validity Period |
|---|---|
| less than 100 km | 1 day from the relevant date |
| For every 100 km thereafter | Additional 1 day from the relevant date |
For example, if a total of 110 km is travelled, then the validity lasts for 1+1=2 days.
In case of Over Dimensional Cargo vehicles| Distance | Validity Period |
|---|---|
| Upto 20 km | 1 day from the relevant date |
| For every 20 km thereafter | Additional 1 day from the relevant date |
If the validity of the e-Way bill has expired, then the goods are not to be moved. Either a fresh bill with all new details must be generated, or another bill can be made with the expired e-Way bill number and new Part B details.
Cancelling And Rejecting e-WAY Bills
Consolidated e-WAY Bills
Masters
A master is a report of all the products, clients, suppliers and transporters frequently dealt with by a user. A separate master can be created for each heading individually.
To generate an e-Way bill, the system asks for information such as customer details and product specifications. Typing this information every time you generate an e-Way bill can become very tedious, which is why masters were introduced.
Bulk Generation Facility
Sub-Users
Blocking/Unblocking of E-Way Bill Generation
Unblocking of e-waybill generation facility means restoring the facility of generation of E Way Bill, in respect of such taxpayers GSTIN (as Consignor or Consignee), in the event of filing of the return for the default period(s), thereby reducing the default period to less than 2 consecutive tax periods.
Also, the Unblocking can be done by the jurisdictional officer online on the GST Portal,upon considering the manual representation received from such taxpayer.
As provided in Rule 138 E of CGST/SGST Rules 2017, blocking of EWB generation facility will be implemented on EWB Portal, when the taxpayer does not file GSTR 3B return for two consecutive tax periods.
Thus, taxpayers who are required to file Form GSTR-3B and have not filed it for the month of January and February, will be blocked from EWB generation facility form March onwards.
In case of filing of GSTR 3B returns by taxpayers, resulting in reduction of their return filing default period of less than two tax periods,their return filing status will be updated on E-Way Bill Portal, and their GSTIN will be unblocked for E Way Bill generation facility, next day.
The Unblocking can be done by the jurisdictional officer online on the GST Portal, upon considering the manual representation received from such taxpayer.
If the tax payer wants to generate the e-way bills immediately, after filing the GSTR 3B Returns(on GST Portal), then theycan login to the e-way bill portal and select the option ‘Search -> Update Block Status‘ and then enter his/her GSTIN and see the status.
If the GSTINis still shown as blocked, then theycan use update optionto get the latest filing status from the GST Common Portal. If their return filing default period is less than two, their return filing status will be communicated by GST System to E Way Bill Portal, and such blocked taxpayers GSTIN will be unblocked and their E Way Bill generation facility will be restored on EWB Portal.
Taxpayersmay contact the GST helpdesk and raise agrievance, if issue is not resolved.
There are two types of transporters –the Transporters who have only enrolled themselves on E Way Bill portal(iewho don’t have GSTIN) and the Transporters who are also registered at GST portal (ie who have GSTIN).
Transportersenrolled in EWB Portalandwho are not registered on GST portal,will not be impacted (as they are not required to file GSTR 3B returns).
If the GSTIN of the GST registered transporter is blocked, then that GSTIN cannot be used as Consignor, Consignee or transporter,while generating e-way bill and updating transporter details.
Yes, the e-way bill system will block the updating of Transporter Id, if registered in GST and has not filed the GSTR 3B Return for last two successive tax periods.
However, there will not be any problem in updating details of the enrolled transporter id(ie who don’t have GSTIN), while generating the e-way bills.
Verification of Vehicle Number
- e-Way Bill GST portal (Documents & FAQs)
- Zoho books
